What is power steering?
There are two main types of automotive steering systems: mechanical steering and power steering. Because the design of the mechanical steering system is relatively simple, and the driver’s physical strength is used as the steering energy, the steering wheel is heavy and difficult to turn, so the power steering system has emerged. The power steering system uses external power to help the driver achieve easy steering, just like the power of the foot on the brake. There are three main types of common power steering systems: mechanical hydraulic power steering system (HPS), electronic hydraulic power steering system (EHPS), and electric power steering system (EPS). Among them, the electronic hydraulic power steering system (EPS) is widely used in commercial vehicles, and the electric power steering system is widely used in passenger cars. As environmental protection becomes stricter, the mechanical hydraulic power steering system and the electronic hydraulic power steering system not only have high power consumption but also have hydraulic oil leakage problems, which do not meet environmental protection requirements. The market share of the two is gradually replaced by EPS.
Components of the Electric Power Steering System
The electric power steering system consists of a steering wheel, a steering shaft, a steering booster, a steering screw, a rubber dust cover and a steering tie rod. Since the steering wheel needs to adjust the angle, a universal joint is also installed on the steering shaft to achieve power transmission at different angles.

How does the electric power steering system work?
There is a steering booster device, which is composed of an electric motor, a torque sensor and an electronic control unit. The power supply in this structure comes from the on-board battery. When the steering wheel is working, the power is transmitted to the steering shaft through the steering wheel. After the torque sensor recognizes the steering angle and steering force, it feeds the data back to the electronic control unit. After analysis and processing, the electronic control unit forms the final power-assist command and sends it to the motor. The motor converts it into different sizes of power-assist voltage according to the command requirements to drive the gear shaft of the motor to rotate. Since the gear shaft and the power-assist gear are meshed, the power will be transmitted to the power-assist gear. The force of the power-assist gear and the driver’s manual steering are superimposed to form the final combined torque, which is finally transmitted to the steering screw through the steering shaft to achieve power steering.
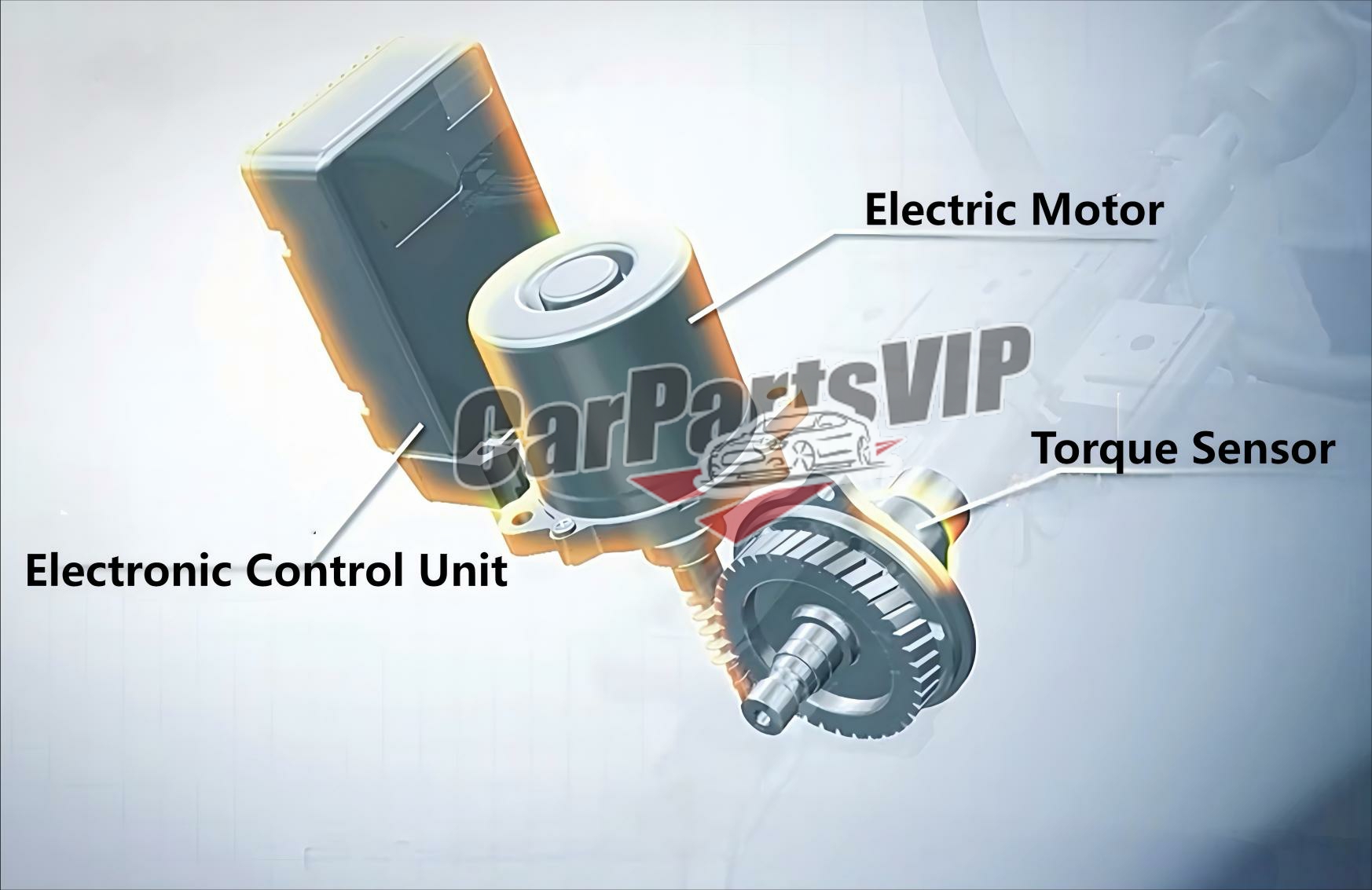
Summary:
Different models on the market have different ways of implementing electric power steering. Some power steering mechanisms are installed at the upper end of the steering shaft, while others are installed at the end of the steering shaft. However, the ultimate goal is to help the driver. The power steering is adjustable with speed, and the controllability is good.



 In order to solve this problem, a rack-and-pinion steering design was developed. A bevel gear, also called a helical gear or steering gear, was added to the end of the steering column. This gear meshes with a rack, which is connected to the front wheel through a steering rod. When the steering wheel is turned, the steering gear drives the rack to move left and right, which drives the rod to push and pull the front wheel to achieve a turn. Due to the addition of racks and pinions in this design, the steering transmission ratio becomes smaller. According to the requirements of the national standard, this ratio is between 12:1 and 24:1. Therefore, for a family car, when the wheel is returned to the correct position, the steering wheel needs to be turned one and a half turns before it can be stopped. In other words, the steering wheel needs to be turned three times from the extreme left to the extreme right. Now you should know why the steering wheel is designed to be round.
In order to solve this problem, a rack-and-pinion steering design was developed. A bevel gear, also called a helical gear or steering gear, was added to the end of the steering column. This gear meshes with a rack, which is connected to the front wheel through a steering rod. When the steering wheel is turned, the steering gear drives the rack to move left and right, which drives the rod to push and pull the front wheel to achieve a turn. Due to the addition of racks and pinions in this design, the steering transmission ratio becomes smaller. According to the requirements of the national standard, this ratio is between 12:1 and 24:1. Therefore, for a family car, when the wheel is returned to the correct position, the steering wheel needs to be turned one and a half turns before it can be stopped. In other words, the steering wheel needs to be turned three times from the extreme left to the extreme right. Now you should know why the steering wheel is designed to be round.